Abstracts
Vol. 2 No. s1 (2025): 48th National Conference of the Italian Association for the Study of Pain
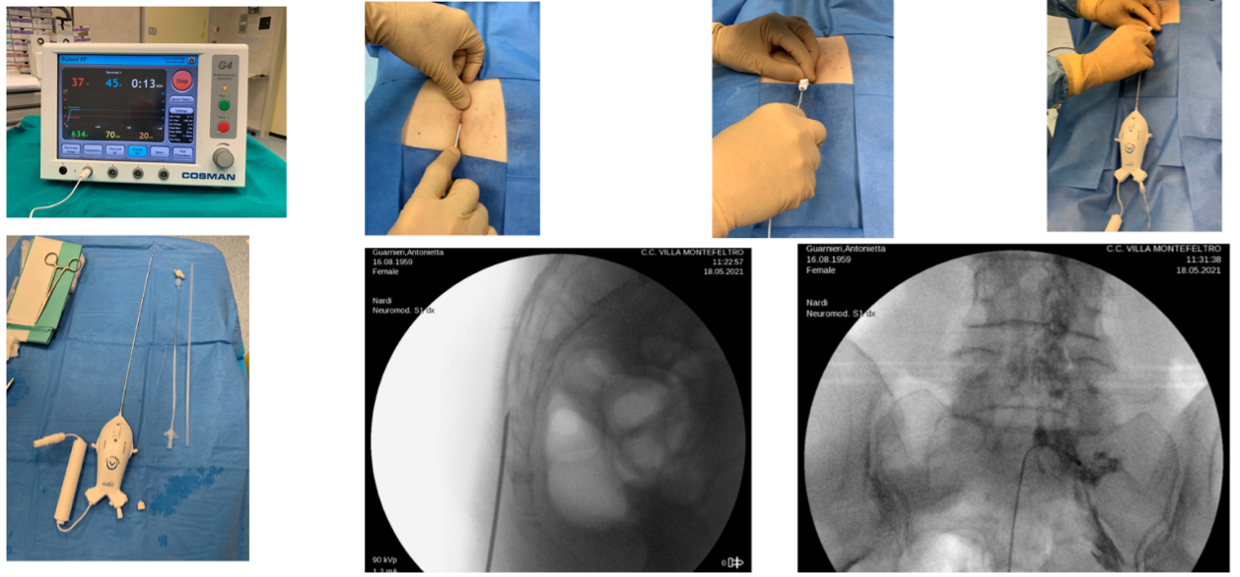
COMBINED USE OF PALMITOYLETHANOLAMIDE + EQUISETUM AND ACETYL L-CARNITINE BEFORE AND AFTER RACZ PERIDURAL ADHESIOLYSIS AND LUMBAR GANGLION NEUROMODULATION
C. Paoletti, L.F. Nardi, F. Del Sordo | Pain Relief Surgery Unit, Casa di Cura Villa Igea, Ancona
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Published: 22 September 2025
85
Views
0
Downloads